What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?
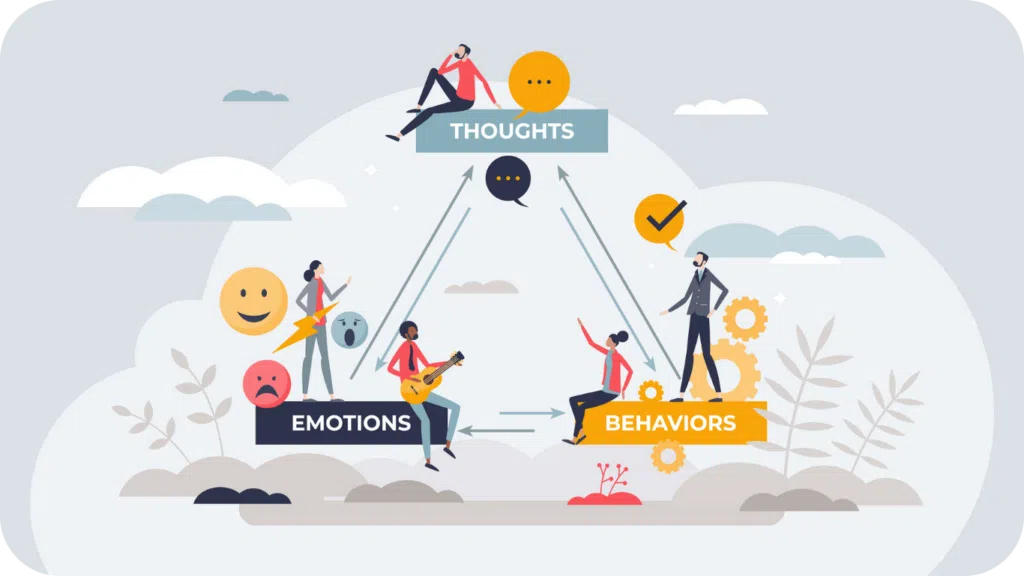
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of talk therapy based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are all connected. Through a structured process and techniques, CBT helps individuals with a range of conditions, from anxiety to self-esteem and anger management.
Read on to learn about the core principles of CBT, how it can help you, and what a cognitive behavioral therapy session looks like.
Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
At its core, CBT helps people by making them aware of the connection between their thoughts, feelings, and behavior. It is a goal-oriented, usually shorter-term therapy. Over time, cognitive behavioral therapists help individuals replace unhelpful or negative thoughts and emotions with more accurate, balanced ones to bring about change.
Cognitive behavioral therapy combines cognitive and behavioral therapies:
- Cognitive Therapy: The core idea is that thoughts influence how we think and feel. CBT helps us to become aware of thoughts, especially those automatic ones we’re not even thinking about.
- Behavioral Therapy: The idea here is that our behaviors also influence how we think and feel. CBT helps you to identify and change unhelpful behaviors.
CBT comes from a combination of these ideas. Thoughts influence actions, and actions influence thoughts. CBT works under the theory that thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are intertwined. This combined approach helps CBT be effective for a wide range of issues.
The Core Principles of CBT
Cognitive behavioral therapy tends to focus on dealing with present-day issues. It’s a “here and now” approach mainly concerned with current problems.
CBT is a goal-orientated therapy that’s based on a few core principles, including:
- Psychological problems are fully or partly rooted in unhelpful thought patterns.
- Psychological problems are fully or partly rooted in unhelpful behavior.
- People with psychological issues can learn better ways to cope, which can help relieve symptoms and improve their well-being.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a collaborative type of therapy that focuses on working with your therapist to identify issues, explore problems, and develop solutions. It’s an active type of therapy where there is a joint effort. Your therapist won’t tell you what to do but will work with you in a structured way to identify and work towards specific goals.
While CBT has core principles, this doesn’t mean that every person will experience the exact same treatment. Therapy needs a tailored approach that factors in each person’s specific needs.
How CBT Works: Techniques and Strategies
Now you know the thinking behind CBT, but how does it actually work?
There are several techniques and strategies a therapist may use in a CBT session. They may use a few of them or just one or two. The exact techniques and strategies can change as CBT is tailored to you and your goals.
Identify and Challenge Negative Thoughts
A therapist can use various techniques to help you become aware of negative thoughts, how they can influence you, and how to challenge them. Cognitive restructuring involves replacing negative or distorted thoughts with realistic, balanced ones. The focus is on accurate thinking.
Let’s take a look at an individual with social anxiety. The automatic thought could be, “I will say something stupid, and everyone will judge me.” The next stage is to think about evidence for and against that thought. Together with a therapist, the individual would develop a more balanced and realistic thought.
Change Unhelpful Behavior
Techniques to modify unhelpful behavior include:
- Exposure Therapy: Often used to treat anxiety disorders. Exposure therapy involves gradually exposing an individual to feared situations in a very safe and controlled environment.
- Skills Training: Learning new coping, social, or problem-solving skills.
Other techniques and strategies used in CBT include teaching:
- Relaxation techniques
- Stress management techniques
- Emotional regulation skills
These are just some of the elements of CBT. A therapist is trained to use the tools and strategies that will be most effective for your specific case.
Specialized Therapy Techniques for Unique Needs
One thing about cognitive behavioral therapy that’s allowed it to be effective for a wide range of issues is its adaptability. There are a number of therapies that are off-shoots of CBT that help with specific issues and others that integrate CBT with other approaches.
Types of therapy within the CBT family include:
- Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP): A core CBT technique highly effective for OCD, involving gradual exposure to obsessions and preventing compulsive responses.
- Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT): A specialized form of CBT designed for trauma survivors, combining CBT with trauma-sensitive approaches.
- CBT for Children and Adolescents: CBT is adapted for younger populations, often using play therapy and family involvement to make it more appropriate.
The following therapies draw heavily from CBT but have evolved into distinct therapies:
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Combines CBT with mindfulness and acceptance strategies, emphasizing emotional regulation and interpersonal effectiveness skills.
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT): Integrates mindfulness meditation practices with CBT techniques.
- Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT): A close relative of CBT that focuses on identifying and challenging irrational beliefs that contribute to emotional distress.
Feeling confused by therapy options? Read this guide on different types of therapy and learn how to choose the best therapy for you.
Conditions Commonly Treated with CBT
CBT has been proven to be effective at helping with a wide range of issues. Its collaborative and structured approach, alongside the focus on the present and developing practical skills that can be used in everyday life, means that it can shine in a number of areas.
Mental health conditions commonly treated with CBT:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Eating Disorders
- Substance Use Disorders
- Sleep Disorders
Emotional issues:
- Anger Issues
- Grief and Loss
- Low Self-Esteem
- Relationship Issues
- Stress Management
CBT can also help people with certain medical conditions, like chronic pain. While therapy doesn’t “cure” a physical illness, it can help improve quality of life by managing symptoms, developing coping skills, and supporting emotional well-being.
Benefits of Choosing CBT for Mental Health
CBT is an evidence-based treatment, which means that it’s supported by extensive research and studies that consistently find that it is effective in helping a range of problems. If you’re considering a certain type of therapy, it’s important that it has a proven record of effectiveness and is backed by scientific research.
A major benefit of CBT is that it aims to provide people with tools to help now and in the future. The idea is that after completing CBT, you can walk away with tools and strategies to improve your coping and support your well-being outside of therapy.
Other benefits of cognitive behavioral therapy include:
- Short-Term: Typically, CBT is a shorter-term therapy, making it more accessible, affordable, and especially helpful for specific issues.
- Reduce Symptoms: CBT helps to reduce the intensity and frequency of distressing symptoms that are often associated with mental health conditions.
- Improve Coping Skills: Part of CBT is to help people develop coping skills so they can deal with stress, anxiety, and other tough emotions more effectively in real life.
- Used with Other Treatments: CBT can be used in combination with other treatments, like medication.
- Flexible: CBT can be used with different populations, such as children, teens, and adults. A CBT therapist can adjust the techniques to your specific needs.
What to Expect During CBT Sessions
You can expect a typical CBT session to last between 45-60 minutes. CBT is a hands-on approach where the therapist and individual collaborate and work together.
Here’s what a typical CBT session looks like:
- Check-In
A CBT session usually begins with a check-in to talk about how you are and how you have been doing since the last session.
- Agenda Setting
Next, you and your therapist will work together to set the agenda for the session and prioritize topics you want to address.
- Homework Review
If your therapist set you homework previously, now is when you would review it together. This could be a journal or behavioral tasks. You can talk about challenges, any insights you have, and successes.
- Working on a Specific Goal or Problem
The core part of the session will include working on the specific goal or problem that you and your therapist have identified. This might involve identifying negative thoughts, challenging thoughts, and behavioral experiments.
- Skills Practice
Your therapist may teach you coping skills or techniques to manage your thoughts, behaviors, and feelings. This could be relaxation techniques, mindfulness exercises, or assertiveness training.
- Set Homework
At the end of a session, you and your therapist figure out what your next homework will be. The idea is that your homework helps you practice any skills you learned in therapy and continue the learning process.
Many CBT treatments fall within the range of 10-20 sessions. Some individuals may notice an improvement in a few sessions, while others may need more or fewer sessions depending on factors like the kind and severity of the problem being addressed. Typically, a CBT session follows a structured framework, but your length of treatment, agenda, goals, skills, and homework will all depend on your unique needs and preferences.
Is CBT the Right Therapy for You?
CBT is a goals-orientated, structured type of therapy that focuses on the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It requires active participation, so it can be a good fit for those who are willing to change patterns, do the work, and be open to feedback.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy might be a good fit for individuals dealing with:
- Anxiety disorders
- Behavioral issues
- Depression
- Relationship problems
- Stress-related issues
Not Sure Where to Start?
If you’re new to therapy, keep an open mind. Your therapist will guide you through what to expect in your first session. They will likely talk you through the initial process, explain their approach to therapy, and help you understand what future sessions will look like.
At Thriving Center of Psychology, we make starting your journey easy. Instead of spending hours researching and contacting therapists, take 5-minutes to fill out our quick and easy questionnaire to get matched with the right therapist for your specific needs. We look forward to starting this journey with you!

The Link Between Social Media and Depression
In today’s world, scrolling through social media is as routine as brushing our teeth. We open apps out of habit — on the train, in bed, while waiting in line. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook keep us connected, informed, and entertained.

Signs Depression is Taking a Toll on Your Relationship
Depression can impact every part of a person’s life, from their work to their romantic relationships. Dealing with depression can take its toll on both the person with depression and the supporting partner. If you’re worried that depression is affecting your relationship, understanding its impact is an important first step.

Anxiety Attack and Panic Attack Differences
’s easy to mix up anxiety and panic attacks. While anxiety attacks and panic attacks do have overlapping symptoms, they are different. Let’s get into the differences between anxiety and panic attacks so you can be in a better position to get the help you need.

How to Overcome Procrastination and Anxiety
Procrastination is a very typical human experience. At some point or another, we’re all guilty of putting off that task we know is important. Maybe it’s household chores, filling your taxes, paying bills, or some other mind-numbingly boring task.

